|
Size: 13312
Comment: No need to repeat qpop when deleting a changeset
|
Size: 13485
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
= Editing history in your repository = First of all, a disclaimer. '''You can't do this'''. At the most basic level, a Mercurial [[Repository|repository]] contains a list of [[ChangeSet|changesets]], each changeset being represented by an [[ChangeSetID|id]], which is the hash of all of the content (data and metadata) of the change, plus the ids of its parents (see also [[Revlog]]). Change the data and the id changes, and so it's a different changeset and no longer part of the original tree of changes. Also, from a workflow point of view, if someone has pulled from your repository, and you try to remove a file from history, then when they push back to you, they push the file you tried to delete and it reappears. You can't put the genie back into the bottle. So even if it's technically possible, it's not possible in a practical sense. |
= Editing History = How to modify repository history. |
| Line 11: | Line 7: |
| == Alternatives to editing history == If you would like to undo a changeset, but don't mind having it preserved in history, you can use the [[http://mercurial.selenic.com/wiki/Backout|hg backout]] command to reverse it. This is generally preferred to changing history as it's non-destructive and lets future developers use that history to avoid making the same mistakes. == Why changing history is hard == First, consider changesets. Each changeset has a changeset id is a cryptographically strong hash of the changeset data, which recursively includes all of the changeset content (data and metadata) as well as the ids of its parents. Change any bit in a changeset itself or the history it's based on and you will change its id. This makes Mercurial changesets tamperproof: it is computationally infeasible to make a tampered changeset that has the same changeset id as a given changeset. Second, Mercurial's network protocol assumes history is append-only. Pushing and pulling only ever add history to repositories, never remove it. If the history you want to modify has already been published to public repositories, there is no way to recall it except with the cooperation of everyone who has pulled a copy, which is generally not practical. == Consequences of editing history == If you edit your repository history, the changeset IDs (i.e., the identity of the changesets) will be changed from the point of the edit forward. Suppose for example that the bad revision is number 3. Then, before your change, the repository will look like this: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 } }}} After your edit, changes `BAD`, `R4` and `R5` will have new changeset IDs: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} As long as nobody else has seen the repository before the change, this is okay. If people have already pulled from your repository, then things become more complex. Suppose someone cloned your repository ''before'' you edited `BAD`, and then pulled afterwards. They would see completeley new changesets, `BADa`, `R4a` and `R5a`, and their tree of changes would look like this: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} This is exactly what one would expect - Mercurial always works this way when you pull in changes from others: It takes two directed acyclic graphs (one representing your repository, the other representing the repository you pull from) and merges common nodes in the graphs to produce a new acyclic graph. Notice that the changesets `R4` and `R4a` and `R5` and `R5a` are identical changes (neither of you edited them), but they have different hash values since they have different histories (because of `BADa`). So you can simply ask your friend to strip `BAD`, which will strip `R4` and `R5` as well - their changes are preserved in `R4a` and `R5a`. This makes your friend's repository identical to yours: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} Furthermore, if your friend had already committed new work on top of `R5`, then his repository looks like this before the pull: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 -> R6 -> R7 } }}} After the pull he gets {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 -> R6 -> R7 R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} Now it is not simply enough to strip BAD since that destroys the work in `R6` and `R7`. But you can ask him to import `R6` and `R7` into MQ, pop the queue, strip BAD and apply the queue again (this time to `R5a`). This is rebasing his changes on `R5'`: {{{ hg qimport -r R6:R7 hg qpop -a hg strip BAD hg update -C R5a # might not be necessary hg qpush -a hg qdelete -r qbase:qtip }}} |
|
| Line 12: | Line 87: |
| Line 23: | Line 97: |
| The key implication is that the changeset IDs will change from the point at which the revision occurs. This means that developers with clones will need to rebase their changes, and care must be taken to manage the effects of the revision. This document does not attempt to cover this process. It assumes that if you need to do this, you will ensure that you know what to do, and you make sure it happens. OK, so you're going to revise history. There are lots of possible revisions: * Remove a change * Collapse a series of changes into one * Edit a commit message * Obliterate a file A similar process can be used for all of these. The simplest approach (as with many things :-) ) is to use the MqExtension. == Using Mercurial Queues == All of the examples above can be handled by MQ: * Remove a change can be achieved using {{{hg qdelete}}} * Collapse a series of changes into one can be achieved using {{{hg qfold}}} * Edit a commit message, obliterate a file, or any other modification of the changes themselves can be achieved using {{{hg qrefresh}}}. To start using Mercurial Queues, you need to have run {{{ hg qinit }}} in the repository. Also, in case the history you edit contains binary files, permission changes or other non-textual changes, enable extended diffs for your repo. Put into {{{.hg/hgrc}}} (or {{{$HOME/.hgrc}}} or some system-wide hgrc) the following section: |
The key implication is that the '''changeset IDs will change''' from the point at which the revision occurs. This means that developers with clones will need to rebase their changes, and care must be taken to manage the effects of the revision. This document does not attempt to cover this process. It assumes that if you need to do this, you will ensure that you know what to do, and you make sure it happens. == Basic changeset removal with clone == One of the simplest tasks is removing the most recent commits in a repository. This can be done non-destructively with clone: {{{ hg clone -r LASTGOODREVISION oldrepo newrepo }}} - and then perhaps move `oldrepo` away as a backup and rename `newrepo` to take its place. If the old repository have multiple heads you might want to pull them too. == Editing recent history with MQ == Recent history can be modified fairly easily with the [[MqExtension|MQ extension]]: * Remove a change with '`hg qdelete`' * Collapse a series of changes into one with '`hg qfold`' * Edit a commit message, obliterate a file, or any other modification of the changes themselves with '`hg qrefresh`' Some caveats exist. First, MQ can't operate on merge changesets. Second, by default MQ works with textual changes. If the history you edit contains binary files, permission changes or other non-textual changes, enable extended diffs for your repo. Add the following section to your ''`hgrc`'': |
| Line 55: | Line 123: |
| Line 60: | Line 129: |
| Those patches are nevertheless still applied, to strip them from the history, you need the {{{qpop}}} command. Issue |
Those patches are nevertheless still applied, to strip them from the history, you need the {{{qpop}}} command. Issue |
| Line 66: | Line 134: |
| Line 70: | Line 137: |
| Line 73: | Line 141: |
| Line 75: | Line 142: |
| Line 80: | Line 148: |
| Line 84: | Line 151: |
| Line 91: | Line 159: |
| Line 95: | Line 164: |
The `qfinish` command turns an applied patch into a real Mercurial changeset. Here we use it to turn all applied patches into normal changesets. One thing this process over-simplifies is that the `hg qpush -a` step may fail, if later changes depend on the obliterated data. In that case, you have to fix the problem manually - there's no easy answer here, after you edit history, you need to manage the consequences, in your own repository as well as elsewhere. So you need to push conflicting patches one by one, edit them as appropriate, and {{{qrefresh}}} the changes. Read [[http://hgbook.red-bean.com/hgbookch12.html|chapter about Mercurial Queues from Mercurial Book]] for details. |
The `qfinish` command turns an applied patch into a real Mercurial changeset. Here we use it to turn all applied patches into normal changesets. One thing this process over-simplifies is that the `hg qpush -a` step may fail, if later changes depend on the obliterated data. In that case, you have to fix the problem manually - there's no easy answer here, after you edit history, you need to manage the consequences, in your own repository as well as elsewhere. So you need to push conflicting patches one by one, edit them as appropriate, and {{{qrefresh}}} the changes. Read [[http://hgbook.red-bean.com/hgbookch12.html|chapter about Mercurial Queues from Mercurial Book]] for details. |
| Line 211: | Line 276: |
| Line 215: | Line 279: |
| Line 218: | Line 281: |
| * If you don't '''really''' need to edit the history (which is probably the case in 99% of all real situations) you should use `hg backout`. This backs out a change by reversing it, ''preserving'' the history - i.e., you can see in hg log that you applied the change, did some other changes, then backed it out. | |
| Line 223: | Line 285: |
| == Consequences of editing history == If you edit your repository history, the changeset IDs (i.e., the identity of the changesets) will be changed from the point of the edit forward. Suppose for example that the bad revision is number 3. Then, before your change, the repository will look like this: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 } }}} After your edit, changes `BAD`, `R4` and `R5` will have new changeset IDs: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} As long as nobody else has seen the repository before the change, this is okay. If people have already pulled from your repository, then things become more complex. Suppose someone cloned your repository ''before'' you edited `BAD`, and then pulled afterwards. They would see completeley new changesets, `BADa`, `R4a` and `R5a`, and their tree of changes would look like this: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} This is exactly what one would expect - Mercurial always works this way when you pull in changes from others: It takes two directed acyclic graphs (one representing your repository, the other representing the repository you pull from) and merges common nodes in the graphs to produce a new acyclic graph. Notice that the changesets `R4` and `R4a` and `R5` and `R5a` are identical changes (neither of you edited them), but they have different hash values since they have different histories (because of `BADa`). So you can simply ask your friend to strip `BAD`, which will strip `R4` and `R5` as well - their changes are preserved in `R4a` and `R5a`. This makes your friend's repository identical to yours: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} Furthermore, if your friend had already committed new work on top of `R5`, then his repository looks like this before the pull: {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 -> R6 -> R7 } }}} After the pull he gets {{{#!dot digraph { rankdir = LR node [shape=box] R1 -> R2 -> BAD -> R4 -> R5 -> R6 -> R7 R2 -> BADa -> R4a -> R5a } }}} Now it is not simply enough to strip BAD since that destroys the work in `R6` and `R7`. But you can ask him to import `R6` and `R7` into MQ, pop the queue, strip BAD and apply the queue again (this time to `R5a`). This is rebasing his changes on `R5'`: {{{ hg qimport -r R6:R7 hg qpop -a hg strip BAD hg update -C R5a # might not be necessary hg qpush -a hg qdelete -r qbase:qtip }}} |
|
| Line 304: | Line 286: |
| * [[ConcatenatingChangesets]] * [[TrimmingHistory]] |
* ConcatenatingChangesets * TrimmingHistory * [[RebaseProject|Rebasing]] |
Editing History
How to modify repository history.
Contents
1. Alternatives to editing history
If you would like to undo a changeset, but don't mind having it preserved in history, you can use the hg backout command to reverse it. This is generally preferred to changing history as it's non-destructive and lets future developers use that history to avoid making the same mistakes.
2. Why changing history is hard
First, consider changesets. Each changeset has a changeset id is a cryptographically strong hash of the changeset data, which recursively includes all of the changeset content (data and metadata) as well as the ids of its parents. Change any bit in a changeset itself or the history it's based on and you will change its id. This makes Mercurial changesets tamperproof: it is computationally infeasible to make a tampered changeset that has the same changeset id as a given changeset.
Second, Mercurial's network protocol assumes history is append-only. Pushing and pulling only ever add history to repositories, never remove it. If the history you want to modify has already been published to public repositories, there is no way to recall it except with the cooperation of everyone who has pulled a copy, which is generally not practical.
3. Consequences of editing history
If you edit your repository history, the changeset IDs (i.e., the identity of the changesets) will be changed from the point of the edit forward. Suppose for example that the bad revision is number 3. Then, before your change, the repository will look like this:

After your edit, changes BAD, R4 and R5 will have new changeset IDs:

As long as nobody else has seen the repository before the change, this is okay. If people have already pulled from your repository, then things become more complex. Suppose someone cloned your repository before you edited BAD, and then pulled afterwards. They would see completeley new changesets, BADa, R4a and R5a, and their tree of changes would look like this:
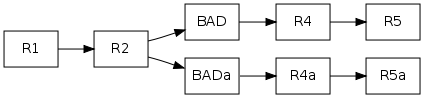
This is exactly what one would expect - Mercurial always works this way when you pull in changes from others: It takes two directed acyclic graphs (one representing your repository, the other representing the repository you pull from) and merges common nodes in the graphs to produce a new acyclic graph.
Notice that the changesets R4 and R4a and R5 and R5a are identical changes (neither of you edited them), but they have different hash values since they have different histories (because of BADa).
So you can simply ask your friend to strip BAD, which will strip R4 and R5 as well - their changes are preserved in R4a and R5a. This makes your friend's repository identical to yours:

Furthermore, if your friend had already committed new work on top of R5, then his repository looks like this before the pull:

After the pull he gets
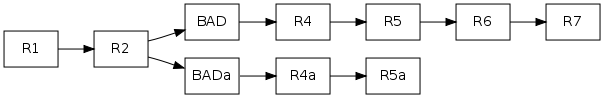
Now it is not simply enough to strip BAD since that destroys the work in R6 and R7. But you can ask him to import R6 and R7 into MQ, pop the queue, strip BAD and apply the queue again (this time to R5a). This is rebasing his changes on R5':
hg qimport -r R6:R7 hg qpop -a hg strip BAD hg update -C R5a # might not be necessary hg qpush -a hg qdelete -r qbase:qtip
4. Motivation
Having said all of this, there are good reasons why people might want to change history. Here are some examples:
- It's a purely personal repository, and you're happy to recreate any branches you made.
- You have a well-controlled development environment, where telling everyone to delete repository copies and re-clone is practical.
- You have strong controls on what gets pulled into the central repository (so you can stop the history being "unrevised") and don't care too much about breaking people's clones.
- Your lawyers insist you do your best to remove something, but they are happy with "reasonable endeavours".
- You have to keep the version history for 5 years, but not longer.
As long as you understand the implications, it is possible to do this.
The key implication is that the changeset IDs will change from the point at which the revision occurs. This means that developers with clones will need to rebase their changes, and care must be taken to manage the effects of the revision. This document does not attempt to cover this process. It assumes that if you need to do this, you will ensure that you know what to do, and you make sure it happens.
5. Basic changeset removal with clone
One of the simplest tasks is removing the most recent commits in a repository. This can be done non-destructively with clone:
hg clone -r LASTGOODREVISION oldrepo newrepo
- and then perhaps move oldrepo away as a backup and rename newrepo to take its place. If the old repository have multiple heads you might want to pull them too.
6. Editing recent history with MQ
Recent history can be modified fairly easily with the MQ extension:
Remove a change with 'hg qdelete'
Collapse a series of changes into one with 'hg qfold'
Edit a commit message, obliterate a file, or any other modification of the changes themselves with 'hg qrefresh'
Some caveats exist. First, MQ can't operate on merge changesets. Second, by default MQ works with textual changes. If the history you edit contains binary files, permission changes or other non-textual changes, enable extended diffs for your repo. Add the following section to your hgrc:
[diff] git = True
(alternatively remember to add --git to every qimport and qrefresh invocation below).
Let's pretend you comitted the file which should not be commited in revision BAD. Then doing
hg qimport -r BAD:tip
will import the changesets into MQ. You can find newly created patches in .hg/patches.
Those patches are nevertheless still applied, to strip them from the history, you need the qpop command. Issue
hg qpop -a
Now all changes since revision BAD are no longer available in your repository history. They are saved as patches in .hg/patches - and only there.
If you want to undo the entire changeset BAD (obliterate it!), then do this:
hg qdelete BAD.diff
If you only want to edit the changeset (remove some edits, avoid commiting one file while leaving the remaining changes etc), then do this:
hg qpush BAD.diff # edit files, remove passwords, revert newly added files etc. hg qrefresh
Note that qdelete removes whole patch, while qrefresh modifies it.
Now if you want to combine the next two patches (say GOOD1.diff and GOOD2.diff) into one patch, do this:
hg qpush GOOD1.diff hg qfold GOOD2.diff
The changes from GOOD2.diff have been integrated ("folded") into GOOD1.diff and the GOOD2.diff patch itself has been deleted from the queue (it can be kept there but unmanaged, by using qfold -k).
To go back to standard Mercurial changesets you do
hg qpush -a hg qfinish -a
The qfinish command turns an applied patch into a real Mercurial changeset. Here we use it to turn all applied patches into normal changesets.
One thing this process over-simplifies is that the hg qpush -a step may fail, if later changes depend on the obliterated data. In that case, you have to fix the problem manually - there's no easy answer here, after you edit history, you need to manage the consequences, in your own repository as well as elsewhere. So you need to push conflicting patches one by one, edit them as appropriate, and qrefresh the changes. Read chapter about Mercurial Queues from Mercurial Book for details.
Here's a real example (captured on Windows). I add a file I shouldn't in revision 1, edit it in revision 2, then try to obliterate revision 1. After doing so, I need to resolve the issue with revision 2 (editing what is now a nonexistent file). In this case it's easy, we just drop revision 2 as well. In other cases, this could be much harder to deal with, possibly even so much harder that you decide it's not worth it. It depends on your data (and possibly your lawyers!).
>hg init >echo Line 1 >a >hg commit --addremove -m "Added a" adding a >rem Add the launch codes for the nuclear arsenal here... >echo Super secret >b >hg commit --addremove -m "Added b" adding b >hg log changeset: 1:65bcb0d3f953 tag: tip user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:43:00 2008 +0000 summary: Added b changeset: 0:5dd6949828e1 user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:42:40 2008 +0000 summary: Added a >rem Here we compound the error... >echo More secret stuff >>b >hg commit -m "Edited b" >echo More safe stuff >>a >hg commit -m "Edited a" >hg log changeset: 3:ea4f8ad48048 tag: tip user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:43:46 2008 +0000 summary: Edited a changeset: 2:6bb0d654a0a6 user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:43:32 2008 +0000 summary: Edited b changeset: 1:65bcb0d3f953 user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:43:00 2008 +0000 summary: Added b changeset: 0:5dd6949828e1 user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:42:40 2008 +0000 summary: Added a >rem We realise our mistake. We need to get rid of changeset 1, >rem so that file b is no longer in out repository! >hg qinit >hg qimport -r 1:tip >hg qpop -a Patch queue now empty >rem Delete changeset 1 >hg qdelete 1.diff >rem Now start to put everything back >hg qpush -a applying 2.diff unable to find 'b' for patching 1 out of 1 hunk FAILED -- saving rejects to file b.rej patch failed, unable to continue (try -v) b: No such file or directory b not tracked! patch failed, rejects left in working dir Errors during apply, please fix and refresh 2.diff >rem Hmm, change 2 depends on file b. Fix things up. Luckily, this is easy, just delete change 2 as well. >rem In reality, change 2 may contain other edits, and we'd need to do some further fixing. >hg qdelete 2.diff abort: cannot delete applied patch 2.diff >rem Even this isn't as simple as all that. Back out change 2 so we can delete it. >hg qpop -a Patch queue now empty >hg qdelete 2.diff >rem And now we're good to go. >hg qpush -a applying 3.diff Now at: 3.diff >hg qdelete -r qbase:qtip >rem No sign of file b, and the world is safe again. >rem Except, of course, that evil Doctor Death pulled from us 5 minutes ago. >rem But at least as we all get blown up, we can be glad that it's not a technical problem :-) >hg log changeset: 1:a50e33884959 tag: tip user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:43:46 2008 +0000 summary: Edited a changeset: 0:5dd6949828e1 user: "Paul Moore <user@example.com>" date: Sat Mar 22 16:42:40 2008 +0000 summary: Added a
The process of going up through the patch stack, tidying up the debris (as in our example, where change 2 wouldn't apply as it depended on the obliterated file "b"), is what is generally referred to as "rebasing" the changes. It can be simple, in the case of a localised change, but it can be arbitrarily complex. Before you start editing history, you need to be sure that you know what to do to rebase.
7. Other options
There are other options that may be more appropriate in particular circumstances.
If you catch your mistake immediately (or reasonably soon), you can just use hg strip REV to roll back the latest (one or more) changes. This produces a bundle of the stripped changes as a backup, so you could strip the changes, then clone and fix up the problem and push the fixes. The effect would be the same as editing history in place, but the window of time for Doctor Death to grab the nuclear codes is limited.
If you want to remove file(s) that shouldn't have been added, use the ConvertExtension with --filemap option to "convert" your Mercurial repository to another Mercurial repository. You'll want to make sure that you set convert.hg.saverev to False if you want to keep in common the history prior to your removed file(s).
To easily reorder, accept, fold or reject changesets there's also the HisteditExtension